How to Ensure Data Privacy and Security in Data Integration Processes
One of the main questions that managers and business owners ask is ‘How to ensure data privacy and security‘ for my data?
In this article, I will try to answer this ever-green question.
Data integration refers to the process of consolidating data from various sources and formats to create a unified and coherent view of the data, enabling organizations to make more informed decisions. However, as the volume of data and the complexity of data sources continue to grow, ensuring data privacy and security has become a critical concern.
Data privacy is the practice of safeguarding sensitive information from unauthorized access, disclosure, or misuse, while data security is a set of measures taken to protect data from unauthorized access, corruption, or loss. These two concepts are closely interrelated and should be addressed together to achieve a comprehensive data protection strategy.
Have you noted how many times we hear about data breaches from the news? Quite a lot, and perhaps there are more to come.
The importance of secure data integration in today’s data-driven world highlights the need for robust privacy and security measures to protect sensitive information and maintain compliance with regulatory requirements while extracting value from data assets.
Further on, we will explore various strategies and best practices for ensuring data privacy and security in data integration processes.
The Importance of Data Privacy and Security in Data Integration
Regulatory Requirements
In recent years, the increasing awareness of data privacy and security issues has led to a surge in regulatory requirements across the globe.
Governments and regulatory bodies have recognized the need to protect the privacy and security of personal and sensitive data, prompting the introduction of strict data protection laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) in the United States.
These regulations impose strict obligations on organizations, requiring them to implement robust data protection measures, obtain explicit consent from data subjects, and be transparent about how data is collected, used, and shared. Failure to comply with these regulations can result in hefty fines, damaged reputations, and loss of customer trust.
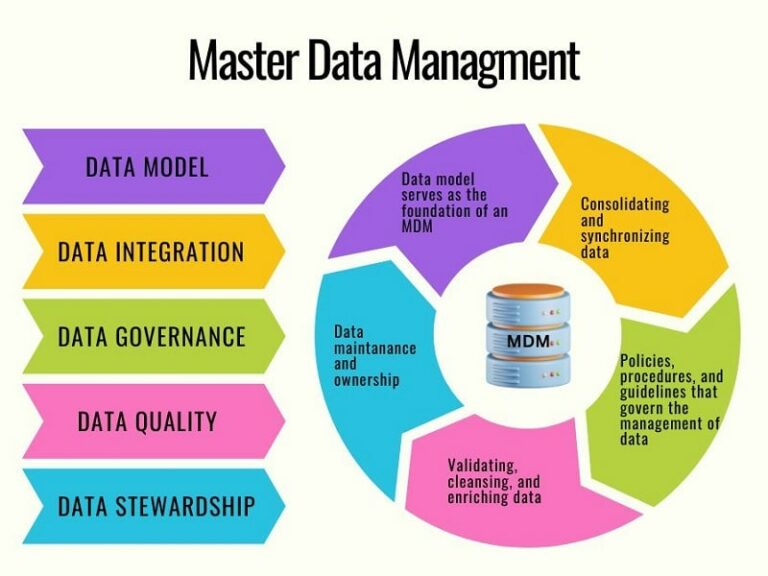
Given the global nature of data integration processes, organizations must be aware of and comply with the various regulations that apply to the data they are handling. This entails implementing proper data management practices, including data classification, data minimization, secure master data management and data storage, to ensure data privacy and security requirements are met.
Risk of Data Breaches
As the volume and complexity of data being collected, stored, and processed by organizations continue to grow, so does the risk of data breaches.
Data breaches can result in the unauthorized access, disclosure, or theft of sensitive information, leading to significant financial and reputational damage for affected organizations. Data breaches can also have severe consequences for individuals whose personal data is compromised, including identity theft and financial loss.
Data integration processes can be particularly vulnerable to data breaches, as they often involve the movement and consolidation of large volumes of data from various sources.
Unauthorized access to this data during the integration process can lead to significant data breaches, putting both the organization and its customers at risk.
Given the severe consequences of data breaches, organizations must prioritize data privacy and security in their data integration processes.
By implementing strong access controls, encryption, data masking, and other security measures, organizations can reduce the risk of data breaches and ensure that their data integration processes remain secure and compliant.
Impact on Customer Trust and Brand Reputation
Ensuring data privacy and security in data integration processes is not only a matter of regulatory compliance but also a crucial factor in maintaining customer trust and building a positive brand reputation.
Customers are increasingly concerned about how their personal information is being handled, and organizations that fail to protect their customers’ data are likely to experience a decline in customer loyalty and trust.
By prioritizing data privacy and security, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to responsible data handling practices, fostering a stronger relationship with their customers and enhancing their brand image.
Technological Advancements and Emerging Challenges
As technology continues to advance, organizations are increasingly faced with new challenges and vulnerabilities in the realm of data privacy and security.
For example, the widespread adoption of cloud-based services, artificial intelligence, and the Internet of Things (IoT) has expanded the attack surface for potential data breaches and created new complexities in data integration processes.
To stay ahead of these emerging challenges, organizations must be proactive in updating their data privacy and security strategies, adapting to new technologies, and investing in employee training and awareness programs.
By understanding and addressing these additional factors, organizations can further appreciate the growing importance of data privacy and security in data integration processes and take the necessary steps to protect their sensitive information and maintain a strong position in the marketplace.
Consequences of Failing to Protect the Data
Fines and Legal Penalties
Failure to protect sensitive information during data integration processes can result in severe financial consequences, particularly if organizations are found to be non-compliant with data protection regulations such as GDPR and CCPA. These regulations impose significant fines on organizations that fail to adequately protect personal data.
For example, under GDPR, companies can face fines of up to 4% of their annual global turnover or $20 million, whichever is higher. Such fines can have a lasting impact on an organization’s financial stability and may even lead to bankruptcy in extreme cases.
Reputational Damage
In addition to financial penalties, organizations that fail to protect sensitive information during data integration processes risk suffering reputational damage.
Data breaches can attract widespread negative media attention, which can harm an organization’s brand image and public perception. Rebuilding a damaged reputation can be a lengthy and costly process, and in some cases, the damage may be irreversible.
Furthermore, a tarnished reputation can make it difficult for organizations to attract new customers, retain existing ones, and secure partnerships with other businesses.
Loss of Customer Trust
The loss of customer trust is another significant consequence of failing to protect sensitive information during data integration processes.
When customers entrust their personal data to an organization, they expect that it will be handled securely and responsibly. If their data is compromised due to inadequate data privacy and security measures, customers may lose trust in the organization and choose to take their business elsewhere.
This can result in a decline in customer loyalty, reduced sales, and difficulties in attracting new customers.
Operational Disruptions
Data breaches and security incidents can also lead to operational disruptions, as organizations must divert resources to investigate the breach, implement remediation measures, and ensure that the affected systems are secure.
Increased Regulatory Scrutiny
Organizations that fail to protect sensitive information during data integration processes may also face increased regulatory scrutiny.
Regulators may impose more stringent reporting and compliance requirements, and organizations may be subjected to more frequent audits and inspections.
This increased scrutiny can put additional strain on an organization’s resources, as they must dedicate time and effort to maintaining compliance and addressing regulatory concerns.
Data Privacy and Security Challenges
Handling Sensitive Data Across Multiple Systems and Platforms
Organizations handling sensitive data across multiple systems and platforms should adopt a holistic approach, using standardized data formats, strong encryption, data masking, and anonymization.
Maintaining a clear understanding of data flow and establishing consistent security policies across all systems is crucial.
Ensuring Data is Protected During Transit and at Rest
To protect sensitive data during transit and at rest, organizations should implement strong encryption techniques.
Use TLS for data in transit and storage-level encryption like AES for data at rest. Regularly update encryption keys and use strong cryptographic algorithms for robust data protection.
Managing Access Controls and Permissions
Implement strict access controls and permissions based on the principle of least privilege. Use role-based access control (RBAC) and multi-factor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized personnel can access sensitive data.
Regularly review and update access controls to maintain a secure data environment.
How to Protect and Secure Your Data
There are many techniques and best practices to protect sensitive information during data integration processes. Let’s list some of them.
Data Classification and Inventory
The first step to securing your data is to perform data classification and inventory.
Identify and categorize the types of data being processed in the integration, such as public, internal, confidential, or restricted.
This helps determine the appropriate levels of protection needed for each data category that you can use in applying various data protection techniques.
Data Minimization
Limit the collection, processing, and storage of personal and sensitive data to what is strictly necessary to fulfil business requirements.
Employ techniques like data deletion, aggregation, and anonymization to minimize the amount of sensitive data being handled during integration.
Data Encryption, Both in Transit and at Rest
- In transit: Use secure communication protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt data while it’s being transmitted between systems. This ensures that even if data is intercepted, it remains unreadable without the appropriate decryption key.
- At rest: Utilize storage-level encryption, such as the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), to protect sensitive data stored in databases or other storage systems. Regularly update encryption keys and employ strong cryptographic algorithms to maintain robust data protection.
Data Masking
Data Masking is a technique that involves replacing sensitive data with fictional or obfuscated data while retaining the original format and characteristics.
Data masking can be used during data integration processes to protect sensitive information without impacting the ability to analyze and process the data.

Data Anonymization
Anonymization techniques remove personally identifiable information (PII) from datasets, rendering them anonymous.
Typical methods include aggregation, generalization, and perturbation. Anonymized data can be safely used for analysis without compromising individual privacy.
Secure Data Storage
Storing sensitive data in a secure storage system is vital for every business. It is important if that system has robust access controls, encryption, and monitoring capabilities.
Regularly patch and update storage systems to address vulnerabilities and maintain the highest level of security.
Backup Solutions
Implement secure backup solutions to protect data against loss, corruption, or accidental deletion.
Encrypt backup data and store it in a separate location from the primary data storage. Periodically test backup and recovery procedures to ensure data can be restored quickly and accurately in case of a disaster.
Regular Security Audits and Monitoring
Conduct periodic security audits to identify potential vulnerabilities and assess the effectiveness of data privacy and security measures.
Implement continuous monitoring to detect and respond to unauthorized access or suspicious activity in real-time.
Data Integration Platforms with Built-In Security Features
Talend
Talend is a popular data integration and transformation platform that offers built-in security features to ensure data privacy and compliance.
Its features include data masking, encryption, and role-based access control.
Talend supports various data sources, including databases, cloud applications, and big data platforms, enabling organizations to seamlessly integrate, transform, and manage their data while maintaining security.
Informatica PowerCenter
Informatica PowerCenter is a widely used data integration platform that offers robust security features, such as secure data transmission using SSL/TLS, data masking, and encryption for data at rest.
PowerCenter also supports role-based access control and detailed auditing to ensure compliance with data privacy regulations. The platform is highly scalable, making it suitable for organizations of all sizes.
IBM InfoSphere
IBM InfoSphere is a comprehensive data integration platform that provides built-in security features, such as data encryption, data masking, and secure communication protocols like SSL/TLS. The platform offers role-based access control, detailed auditing, and monitoring capabilities to ensure data privacy and compliance with regulatory requirements. InfoSphere supports a wide range of data sources and offers advanced data transformation and cleansing features.
Microsoft Azure Data Factory
Azure Data Factory is a cloud-based data integration platform that offers built-in security features, such as encryption for data at rest and in transit, secure data storage using Azure Storage Service Encryption, and managed private network connectivity.
The platform supports role-based access control and auditing, allowing organizations to ensure data privacy and security complies with regulatory requirements.
Azure Data Factory supports various data sources and enables seamless integration with other Azure services.
SAP
SAP Data Services is an enterprise-grade data integration platform that provides built-in security features to protect sensitive information during data integration processes.
It offers data masking, data encryption, and secure communication protocols to safeguard data in transit and at rest.
The platform supports role-based access control and detailed auditing to maintain compliance with data privacy regulations.
SAP Data Services is compatible with a wide range of data sources, including databases, cloud applications, and big data platforms.
These data integration tools and platforms with built-in security features help you streamline your data integration processes while ensuring data privacy and compliance with regulatory requirements.
Note, the above platforms are just a fraction of the tools that are available on the market.
How to Ensure Data Privacy and Security – Summary
In conclusion, ensuring data privacy and security during data integration processes is of paramount importance in today’s data-driven world.
As organizations increasingly rely on data to drive decision-making, innovation, and growth, it is crucial to implement robust data protection measures to maintain compliance with regulatory requirements, preserve customer trust, and protect sensitive information from unauthorized access or theft.
Failing to protect sensitive information during data integration processes can lead to severe consequences, including financial penalties, reputational damage, loss of customer trust, operational disruptions, and increased regulatory scrutiny.
By adopting best practices, utilizing data integration tools with built-in security features, and prioritizing data protection throughout the data integration process, organizations can mitigate these risks and safeguard their sensitive information.
As you continue to navigate the complex landscape of data privacy and security in the context of data integration, I encourage you to explore other supporting posts related to data integration.