Master Data Management: Ensuring Data Consistency and Quality Across Systems
Master Data Management is a well-known topic and every significant business wants to have MDM implemented.
Why?
Master Data Management stands for quality as it centralises all major business entities in one system giving the business users one unified view that can be used in business intelligence reporting tools.
MDM guarantees consistency, accuracy and quality throughout all integrated systems.
This sounds awesome, but implementing MDM is not an easy task.
As a data integration expert, I’ve had the privilege of witnessing the transformative power of Master Data Management (MDM) for many businesses.
In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating realm of Master Data Management, touching on its significance and providing real-world examples that demonstrate its potential to revolutionize your data management practices, ultimately propelling your business toward greater success.
What is Master Data Management?
Master Data Management, or MDM, is a comprehensive approach to identifying, consolidating, and maintaining the most essential data within an organization, known as master data.
This data typically includes information about customers, products, suppliers, employees, and other critical entities that drive business operations.
The purpose of MDM is to create a single, unified, and accurate source of truth for your organization’s master data, which can then be leveraged across various systems, departments, and processes.
The primary goals of MDM include eliminating data inconsistencies, reducing errors, and improving overall data quality.
Also, enhancing data security and privacy for master data management is a critical aspect of safeguarding sensitive information and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
This sound really good, but how it looks in real life? Let me explain with an example.
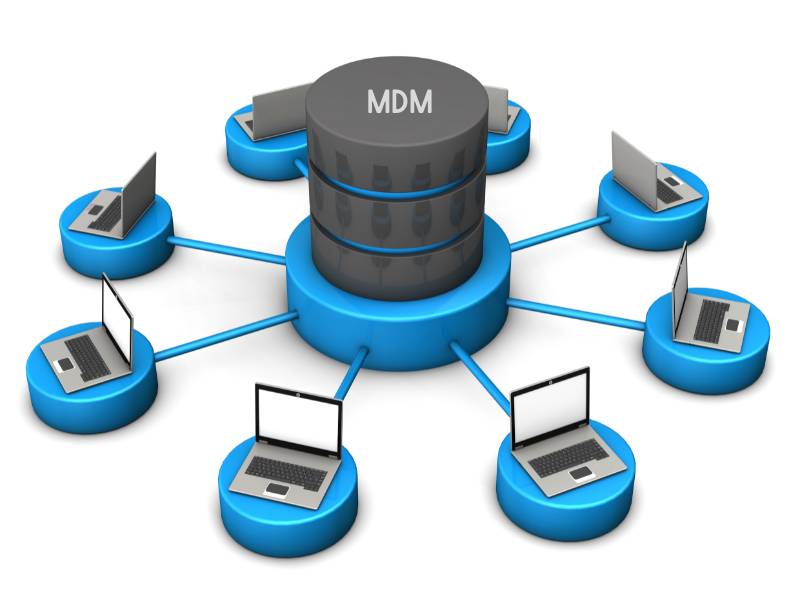
Master Data Management – Simple Example
Let’s say there is employee data stored in a few different systems like HR, Payroll, and CRM.
Business managers want to get all employee information in one place so they can report on them. MDM system is ready to consume all the information and store all employee attributes in one unified table.
But what happens if the same attributes come from more than one table? For instant ‘First Name’ or ‘Last Name’.
Typically what happens is that each system you integrate with has authority over some data while others don’t. For example, we know that ‘First Name’ and ‘Last Name’ should always be correct in the HR system, so we always take it from there and ignore other systems.
Another example is Payroll ID which always comes from Payroll. Even if the same Payroll ID can be found in HR or CRM it is ignored as Payroll has authority over this field in the entire business.
Non-critical fields (attributes) can be updated in MDM from whatever systems they come from. It all depends on the MDM rules that are set in the system.
Obviously, there is more to it, but for simplicity, it works like this.
What are The Main Components of the MDM System?
An effective MDM system is composed of several key components that work together to create a cohesive and efficient data management framework. These components include:
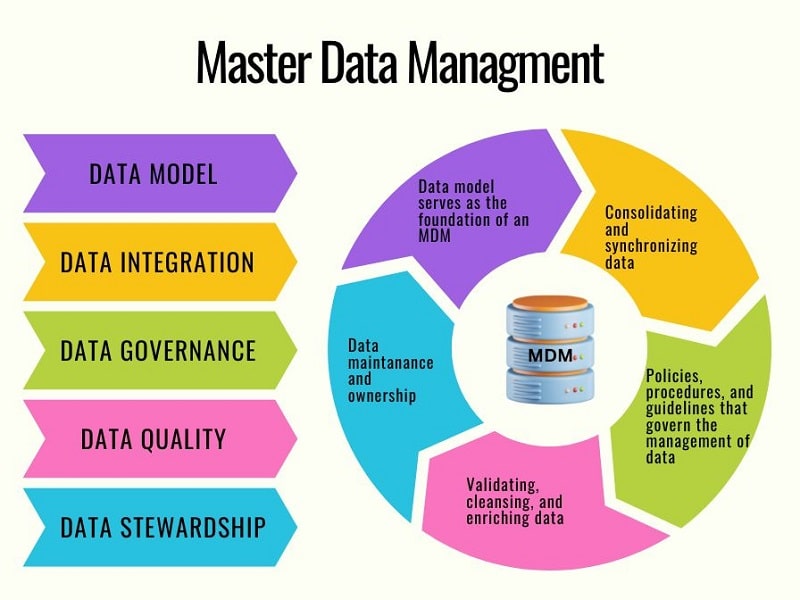
Data Model
A data model serves as the foundation of an MDM system, defining the structure and relationships between various types of master data.
It provides a blueprint for organizing, storing, and retrieving master data, making it easier to understand and use across the organization.
Data Integration
This component is responsible for consolidating and synchronizing master data from multiple sources, such as databases, applications, and external systems.
Data integration techniques, like Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) and data virtualization, enable a seamless flow of information, ensuring that your MDM system remains up-to-date and accurate.
Data Governance
Data governance encompasses the policies, procedures, and guidelines that govern the management of your master data.
It defines the roles, responsibilities, and decision-making processes related to data ownership, data quality, and data access, helping to maintain consistency and integrity across the organization.
Data Quality
Ensuring data quality is a fundamental aspect of MDM.
This component involves processes and technologies for validating, cleansing, and enriching master data.
Data quality tools help identify and resolve inconsistencies, errors, and duplications, ultimately improving the reliability and accuracy of your master data.
Data Stewardship
Data stewards are responsible for overseeing the proper use, maintenance, and improvement of master data.
They act as intermediaries between business users and technical teams, ensuring that data is handled according to established policies and guidelines, while also identifying opportunities for enhancements.
Master Data Management Best Practices
Implementing an effective Master Data Management system requires careful planning and execution. To help guide you on this journey, here’s a list of best practices for MDM implementation:
Defining a Clear MDM Strategy and Objectives
Begin by identifying your organization’s specific goals and objectives for implementing MDM. This may include improving data consistency, enhancing decision-making, streamlining operations, or ensuring regulatory compliance.
A well-defined strategy will provide direction and focus throughout the implementation process.
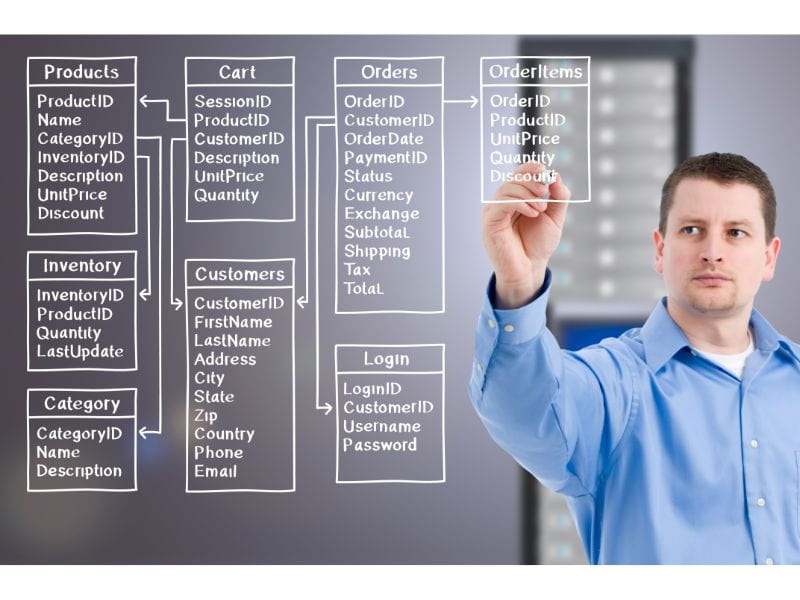
Establishing Data Governance Policies and Procedures
Develop a robust data governance framework that outlines the policies, procedures, and guidelines for managing master data.
This should include clear roles and responsibilities for data ownership, data stewardship, and data access, as well as standards for data quality and consistency.
Consider using governance tools like Microsoft Purview to collect all metadata and set the governance rules.
Selecting the Right MDM Tools and Platforms
Evaluate various MDM solutions to determine the best fit for your organization’s needs and requirements. Consider factors such as scalability, flexibility, ease of use, and integration capabilities when making your selection.
The right MDM platform will enable you to efficiently manage and maintain your master data.
MDM platforms are usually very expensive and can be very complex. Selecting one is not an easy task. Look for a well-known brand that is simple to understand and maintain.
Ensuring Data Quality through Data Profiling, Cleansing, and Validation
Prioritize data quality by incorporating data profiling, cleansing, and validation processes into your MDM implementation.
These techniques help identify and resolve data inconsistencies, errors, and duplicates, ensuring that your master data remains accurate and reliable.
These tasks are usually performed by a dedicated data integration team.
Continuously Monitoring and Improving MDM Processes
MDM is not a one-time project but an ongoing commitment to maintaining and enhancing the quality of your master data.
Establish a monitoring and reporting framework to track the performance of your MDM system, identify areas for improvement, and take corrective actions as needed.
This will ensure that your MDM processes remain agile and effective in the face of evolving business needs and challenges.
MDM – List of Popular Platforms
Here’s a brief overview of three popular Master Data Management platforms that can help you streamline your organization’s data management processes:
Informatica is a leading provider of MDM solutions, offering a comprehensive, modular, and scalable platform to address various data management needs.
The Informatica MDM suite provides powerful capabilities for data integration, data quality, data governance, and data stewardship.
Its flexible and customizable architecture allows organizations to implement tailored MDM solutions that align with their specific requirements and objectives.
With its robust functionality and extensive support for industry standards, Informatica MDM has become a popular choice for organizations across a wide range of sectors.
SAP Master Data Governance (MDG) is an integrated, end-to-end MDM solution designed to work seamlessly with SAP’s suite of enterprise applications.
SAP MDG provides a centralized platform for managing and maintaining master data across various domains, such as customers, suppliers, materials, and finance.
It offers powerful data governance, data quality, and data integration features, along with pre-built workflows, rules, and data models to streamline the MDM process.
With its deep integration into SAP’s ecosystem, SAP MDG is an excellent choice for organizations that rely heavily on SAP applications and infrastructure.
IBM InfoSphere MDM is a comprehensive, enterprise-grade MDM solution that helps organizations create and maintain a single, trusted view of their master data.
The platform offers robust capabilities for data integration, data quality, data governance, and data stewardship, with support for both on-premises and cloud deployments.
IBM InfoSphere MDM includes pre-built data models, rules, and workflows, as well as advanced analytics and machine learning features to enhance data quality and streamline data management processes.
Its flexible architecture and compatibility with various data sources make IBM InfoSphere MDM a versatile option for organizations of all sizes and industries.
Talend is a well-known provider of data integration and data management solutions, including a powerful MDM platform.
Talend MDM offers a comprehensive set of features for data modelling, data governance, data quality, and data integration, all within a user-friendly, web-based interface.
The platform provides real-time data synchronization, support for various data sources, and built-in data stewardship capabilities.
With its open-source foundation, Talend MDM is known for its flexibility and cost-effectiveness, making it an attractive option for organizations looking for a scalable and customizable MDM solution.
Semarchy xDM is an innovative MDM platform that uses a unique approach called Intelligent Data Hub to manage and maintain master data.
This approach allows organizations to model, govern, and share master data across multiple domains, applications, and systems in a unified, collaborative environment.
Semarchy xDM offers powerful data governance, data quality, and data integration features, as well as advanced analytics and machine learning capabilities to optimize data management processes.
With its intuitive interface, agile methodology, and a strong focus on collaboration, Semarchy xDM has gained popularity among organizations looking for a modern, flexible, and user-friendly MDM platform.
Read more about other Master Data Management platforms.
Can you Implement MDM by Yourself?
During my career, I experienced companies that tried to create their own, in-house MDM system. Did it work? Actually yes, but why?
MDM can be implemented on a small scale in a business that does not have many complicated systems and where defining MDM rules is a simpler task.
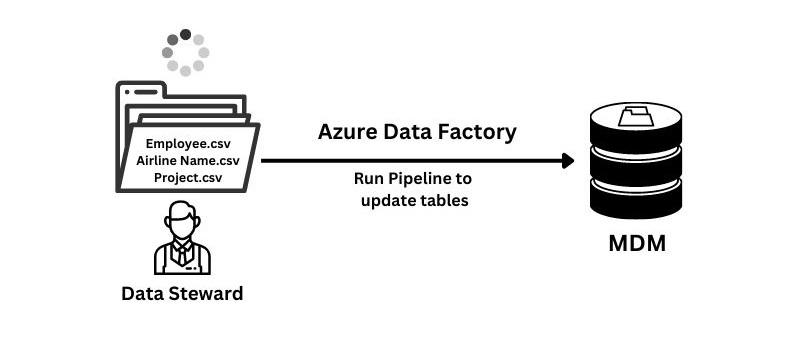
It can be as simple as this:
– brainstorm what are the main categorical business entities
– define a network folder repository to store entity files
– in the CSV/excel files store the data, e.g. Airline Names, Partner Names, System Codes, etc.
– assign Data Stewards to maintain the files; if they make an update the tell data integration team to reload newly updated entity data and refresh the reports.
The above example can be used to maintain simple categorical dimensions that can be used in reporting. If the task gets too complex, definitely look for a proper MDM platform.
Master Data Management – Summary
By implementing a robust MDM strategy, you can harmonize and synchronize your master data, thus eliminating data discrepancies, improving decision-making, and fostering collaboration.
With a solid MDM foundation, you’ll be well-equipped to navigate the complexities of the modern data landscape and make the most of your valuable data assets.
As you embark on your MDM journey, take the time to assess your specific needs, establish robust data governance policies, select the right MDM tools and platforms, and commit to continuous improvement.
By doing so, you will harness the true potential of your organization’s data and drive lasting success in the increasingly data-driven business world.
Stay tuned for more talks in the data integration space as we will cover all aspects of data integration.